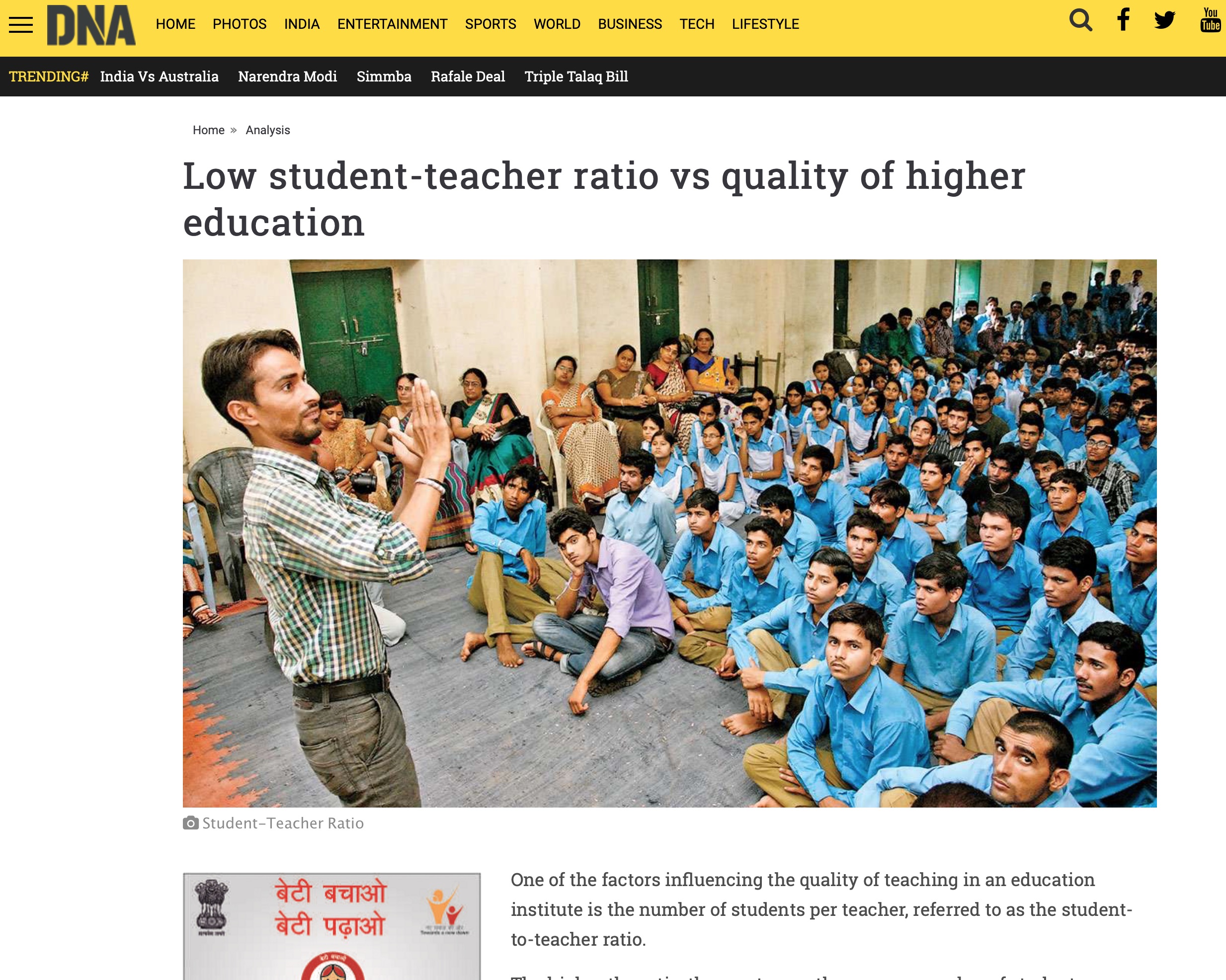
The use of automation was one of the trends that was accelerated by the pandemic. The adoption of Artificial Intelligence (AI) is not limited to businesses, but economies have also turned their focus on building up their AI capabilities as a means to augment growth. Developed economies like the U.S, China and EU countries are already in the race. Now, India too is set to join them. In the last couple of years, the Government of India established a Task Force on Artificial Intelligence and mandated the NITI Aayog to prepare a National strategy on AI with a view to leverage AI for inclusive growth. However, AI adoption remained at a nascent stage in India. India’s first Artificial Intelligence summit, Responsible AI for Social Empowerment (RAISE) 2020 has turned the possibility of AI adoption into an imminent reality.
Amidst the accelerated adoption of AI-based technologies, India seems to stand at the precipice of the fourth industrial revolution. The competitive advantage of low-cost labour may fade away in the near future as economies begin to reap the benefits of AI in the form of increased productivity and cost advantages, and become more profitable than labour. Hence, it would be a timely move for India to build its AI capabilities, lest the global digital divide widens even more and we are left behind.
The report titled “Rewire for Growth” by Accenture estimates that AI has the potential to add US$ 957 billion to India’s economy in 2035. As the post-COVID economy begins to rebuild itself, AI will present an opportunity to leapfrog by opening up newer sources of value and growth, beyond the physical limitations of capital and labour. However, AI elicits excitement and apprehension in equal measures. As much as AI and machine learning (ML) hold immense possibilities for the future of economy, there are a number of issues and apprehensions surrounding it, and one of them is job displacement and by extension, unequal growth.
The skill-biased technological changes in the past have been assumed to be the cause for rising wage inequality. Contrary to this assumption, technological advancements have proven to be beneficial for everyone in the long-run. Since the first industrial revolution and up to the advancement in the information technology now, the world has only stood to gain more. AI is only one of the many phenomena that have disrupted economies and the way we work. according to experts, AI, like any other new technology in the past, will create more jobs than it destroys. Since we look at employment from the narrow confines of existing jobs, it limits our understanding of the extent of impact that AI can have in generating employment.
Moreover, AI will penetrate more broadly because of the ML processes, wherein systems progressively learn and improve their performance with time. Thus, government interventions as well as private sector innovations will be instrumental in steering AI to create equitable growth. While there are positive cascading effects to realise in the future, the past technological changes show that newer technologies are often accessible only to the wealthy. The past couple of decades have also showed that innovation can democratize the access of such newer technologies. The mobile phone and the internet are two examples of such technological advancements whose cost went down enough to reach the larger population. The continued innovation by businesses made it possible to lower the cost of these entities that were once considered a luxury, and India was able to usher a digital revolution.
Nevertheless, initial adoption of a technology has its sets of challenges, and more so for the developing economies. The limited access to the select few can widen the income inequality, and the transformation phase of adoption is likely to replace some jobs before it generates them. In a developing economy like India that has an overflowing labour market coupled with unemployment, the transition could become particularly difficult. While historically, newer technologies have proven to be beneficial in the long-run, the short-term losses cannot be justified. The onus however lies on the policies rather than the technology. Governments in the past could not anticipate the comprehensive impact of technological revolutions, but the GoI’s focus on responsible AI should allay such fears with respect to governance.
AI is one of the many tools that can be used to either bridge the inequalities or create more. To achieve the former, the right policy approach and business practices at the outset are crucial for cushioning the negative externalities. Hence, a collaborative approach is the first step to realise the vision of AI-driven equitable growth. The knowledge gap could become the biggest impediment for designing policies for the futures, and therefore, the government, the industry and the academia are three spheres that need to work synergistically to bridge that knowledge gap. With technologies progressing much faster than they used to in the last century coupled with the pandemic-induced threats to the economy, the policymakers cannot design policies fast enough unless an AI ecosystem is built with the industry and academia as vital partners.
The collaborative efforts are the key to accelerate technology diffusion by promoting innovations that democratize the access of new technologies, enhancing research and development in AI that address the issues of data protection, transparency and accountability so that it gains public trust and encourages greater investment. With greater inclusion of stakeholders and greater diversity at each step of building an AI ecosystem, India can look to reap the gains of automation in not only the long-run, but also the short-run.
The article was published with Economic Times on October 9, 2020.